What is the Diabetes Honeymoon Period?
The diabetes honeymoon period, also known as the remission phase, is a fascinating and often welcome experience for individuals newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. It’s a period, typically lasting from a few weeks to a year or more, where the body retains some ability to produce insulin, leading to a temporary reduction in the amount of insulin needed to manage blood sugar levels. This can mean fewer insulin injections, more stable blood sugar readings, and an overall improved sense of well-being. It’s important to understand that the honeymoon phase isn’t a cure, but rather a temporary reprieve. The body’s immune system continues to attack the insulin-producing cells (beta cells) in the pancreas, though at a slower rate during this time. Therefore, careful management and monitoring are essential to maintain health and prepare for the eventual decline of this phase.
Symptoms of the Diabetes Honeymoon Phase
Identifying the symptoms of the diabetes honeymoon phase is critical for effective management. The most noticeable sign is often a significant improvement in blood sugar control. This means fewer high and low blood sugar episodes and more consistent readings within the target range. Another key symptom is a reduced need for insulin. The daily insulin dosage may decrease considerably, and some individuals might even experience a temporary cessation of insulin injections. Simultaneously, there’s often a notable boost in energy levels, with the individual feeling less fatigued and experiencing an overall improvement in physical vitality. Furthermore, the honeymoon phase can also manifest as a reduced risk of diabetes complications, such as frequent infections or skin problems. Recognizing these symptoms early can significantly aid in adjusting treatment plans and ensuring optimal health during this period.
Improved Blood Sugar Control
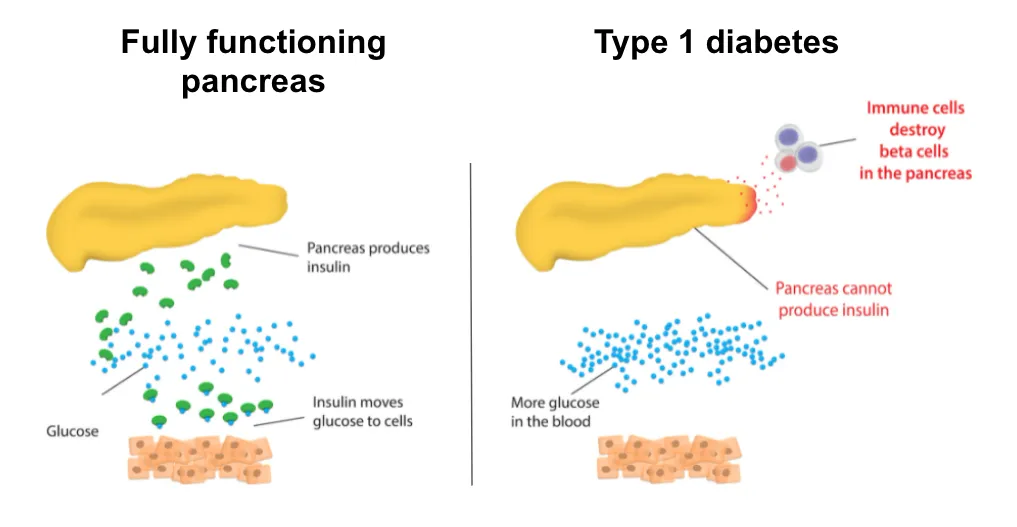
One of the most significant signs of the diabetes honeymoon phase is the noticeable improvement in blood sugar control. This means blood glucose levels become more stable and predictable. Individuals often experience fewer instances of hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Regular blood glucose monitoring will reveal readings consistently within the target range set by the healthcare provider. Moreover, the variability in blood sugar readings tends to decrease, providing a clearer picture of overall metabolic health. This improved control not only enhances the individual’s physical well-being, but also reduces the long-term risks associated with diabetes, such as cardiovascular disease and nerve damage. The ability to maintain steady blood sugar levels is a key indicator of the honeymoon phase and a positive sign of the body’s ongoing response to treatment.
Reduced Insulin Needs
A hallmark of the diabetes honeymoon phase is a significant reduction in insulin requirements. As the body’s own insulin production partially recovers, the external insulin dosage needed to manage blood sugar levels decreases. This may involve a reduction in the number of daily injections or the dosage amount. Some individuals may even temporarily stop using insulin altogether. It’s crucial to work closely with a healthcare team during this period to carefully monitor blood sugar levels and adjust insulin doses accordingly. The reduction in insulin needs isn’t a signal to discontinue diabetes management, but an opportunity to fine-tune the treatment plan. Regular check-ups and blood sugar monitoring are key to ensure the optimal balance between insulin and lifestyle adjustments for overall health and well-being.
Increased Energy Levels
During the diabetes honeymoon phase, many individuals report a significant increase in energy levels. With blood sugar levels better regulated, the body’s cells can more efficiently use glucose for fuel, leading to reduced fatigue and improved overall vitality. This renewed energy allows people to be more active, participate in their favorite activities, and experience a greater sense of well-being. Sleep quality often improves, and individuals may find it easier to concentrate and focus. The boost in energy is a tangible benefit of the honeymoon phase and a strong motivator for maintaining healthy habits, like consistent blood sugar monitoring, a balanced diet, and regular exercise. This positive energy also plays a crucial role in managing the emotional and psychological aspects of living with diabetes.
Fewer Diabetes Complications

The diabetes honeymoon phase often brings about a welcome reduction in the frequency and severity of diabetes-related complications. With improved blood sugar control, the risk of both short-term and long-term complications decreases. Individuals may experience fewer infections, such as skin infections or urinary tract infections, as well as reduced instances of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a serious condition resulting from uncontrolled blood sugar. In the long term, tighter blood sugar control during the honeymoon phase can help minimize the risk of chronic complications like nerve damage (neuropathy), eye damage (retinopathy), and kidney damage (nephropathy). This phase offers a valuable opportunity to establish a foundation of health and minimize the impact of diabetes on overall well-being. Consistent monitoring and proactive management are crucial during this period to maximize these benefits and protect overall health.
How Long Does the Honeymoon Period Last?
The duration of the diabetes honeymoon period varies significantly from person to person. For some, it may last only a few weeks or months, while others may experience it for a year or longer. There is no set timeframe, and the length of the honeymoon phase depends on multiple factors including the individual’s age, the initial severity of diabetes, and the effectiveness of their treatment plan. It is important to remember that the honeymoon phase is temporary. The body’s ability to produce insulin will gradually decline as the immune system continues to attack the beta cells. As the honeymoon period comes to an end, the need for insulin will gradually increase again. Therefore, a proactive approach to management and a clear understanding of the phase’s progression are critical for individuals living with diabetes.
Factors Influencing the Honeymoon Phase
Several factors can influence the duration and intensity of the diabetes honeymoon phase. Early and aggressive insulin therapy, especially soon after diagnosis, has been shown to help preserve beta-cell function and extend the honeymoon period. A healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight, also plays a vital role. Consistent monitoring of blood sugar levels and prompt adjustments to treatment plans, based on the guidance of a healthcare team, are also crucial. Genetic factors and the individual’s immune response also contribute to the duration and character of the honeymoon phase. People who actively manage their diabetes, following medical advice and adopting healthy habits, tend to experience a longer and more effective honeymoon period, improving their quality of life.
Managing Diabetes During the Honeymoon Period

Effective management during the diabetes honeymoon phase involves a multi-faceted approach centered on proactive care and close collaboration with a healthcare team. While insulin needs may be reduced, it’s important to continue monitoring blood sugar levels regularly. This helps to track fluctuations and to make necessary adjustments to insulin doses or other medications. A healthy diet, with a focus on portion control, complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and plenty of fruits and vegetables, is another important component. Regular exercise is also critical, as physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity and help maintain stable blood sugar levels. Maintaining an active dialogue with healthcare providers, including endocrinologists, diabetes educators, and dietitians, is essential to ensure the best possible outcomes and help with ongoing adjustments to care.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regular blood sugar monitoring is the cornerstone of diabetes management during the honeymoon period. This involves checking blood glucose levels at various times throughout the day, as recommended by a healthcare professional. The frequency of testing may vary, but typically includes before meals, after meals, and before bedtime. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) offer real-time glucose data and can provide valuable insights into blood sugar trends. Keeping a detailed record of blood sugar readings, along with information about meals, exercise, and medications, is extremely helpful in identifying patterns and making informed decisions. This data is essential for adjusting insulin dosages and other treatments as needed, ensuring optimal blood sugar control and maximizing the duration of the honeymoon phase. Regular monitoring enables individuals to stay informed about their health and proactively manage their diabetes.
Healthy Diet and Exercise
A healthy diet and regular exercise are fundamental to managing diabetes during the honeymoon period. Focus on a balanced diet that emphasizes whole grains, lean proteins, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. It’s also essential to limit your intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive amounts of saturated and trans fats. Meal timing and portion control can have a significant impact on blood sugar levels. Incorporate regular physical activity into your routine. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Exercise improves insulin sensitivity and helps lower blood sugar. Combine both aerobic and resistance exercises to maximize the benefits. Make any necessary adjustments to your diet and exercise plan in consultation with your healthcare team to align with your treatment plan, blood sugar levels, and overall health goals.
Medication Adjustments

During the diabetes honeymoon phase, medication adjustments are often necessary to effectively manage blood sugar levels. Insulin dosages may need to be reduced as the body starts producing its own insulin. Healthcare providers will carefully monitor blood sugar levels and make adjustments to insulin regimens, in consultation with the individual. The medication adjustments should be based on regular blood glucose monitoring, changes in diet and exercise, and any other lifestyle modifications. It’s important to communicate any changes in blood sugar patterns or symptoms to the healthcare team promptly. Make sure to follow all the provided instructions to ensure medication is effective. Work with the healthcare team to fine-tune the treatment plan and provide better outcomes for your health and well-being.
Tips for Maintaining Good Health After the Honeymoon
After the diabetes honeymoon period ends, it’s crucial to maintain a proactive approach to managing diabetes to safeguard long-term health. Continue to prioritize regular blood sugar monitoring, and communicate with your healthcare provider regularly. Maintain a healthy diet, focusing on a balanced intake and controlled portions. Stay committed to regular physical activity, combining both aerobic and resistance exercises. Adhere to all prescribed medications and continue to adjust dosages as instructed by your healthcare team. Regular check-ups and screenings are vital to catch and manage any potential complications early. Finally, prioritize mental and emotional well-being, which plays a crucial role in maintaining good health and overall quality of life. By embracing these habits, you will reduce complications and foster a good life.
