What is the Type 1 Diabetes Honeymoon Phase?
The honeymoon phase, also known as the remission phase, is a temporary period following the diagnosis of type 1 diabetes. This phase is characterized by a period where the body’s insulin needs are significantly reduced, and blood glucose levels are easier to manage. This phase can bring a sense of relief and optimism after the initial shock of diagnosis. However, it is essential to understand that this phase is transient, and the need for insulin will eventually increase again. Understanding the honeymoon phase helps patients and their families to be prepared and manage their diabetes effectively throughout this transition. Managing diabetes during this time requires careful monitoring, adjustments to treatment, and a supportive care team to navigate the changes and maintain overall health. It is a critical period where proper understanding can significantly improve long-term diabetes management.
Defining the Honeymoon Phase
Defining the honeymoon phase involves understanding it as a period of remission that follows the diagnosis of type 1 diabetes. During this phase, the patient may experience reduced insulin needs, which can lead to improved blood sugar control and fewer insulin injections. It is important to know that this is not a cure, and the body’s ability to produce insulin will continue to decline over time. Recognizing and understanding the characteristics of the honeymoon phase can help patients and healthcare providers manage diabetes during this period and adjust treatment plans accordingly. The honeymoon phase varies from person to person, making it crucial to monitor individual responses to treatment and provide personalized care. Being aware of the potential for remission can help manage expectations and support the emotional well-being of those living with type 1 diabetes.
Typical Duration of the Honeymoon Phase

The duration of the honeymoon phase can vary considerably from a few weeks to several months, and in rare cases, even longer. It is difficult to predict how long this phase will last, as it is influenced by various factors, including the age of the patient, the initial severity of the disease, and the treatment approach. During the honeymoon phase, the pancreas still produces some insulin, leading to reduced insulin requirements. This period of remission is temporary, and insulin needs will eventually increase as the body’s ability to produce insulin declines further. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and adjustments to insulin dosage are necessary to manage diabetes effectively. The healthcare team and the patient must work closely together to adapt to changing insulin requirements. Understanding that the duration varies is essential to manage expectations and maintain effective diabetes care throughout this transitional period, ensuring patient well-being and long-term health.
Top 5 Facts About the Type 1 Diabetes Honeymoon Phase
Fact 1 Insulin Needs Reduce
One of the primary characteristics of the honeymoon phase is a significant reduction in insulin requirements. After the initial diagnosis and insulin therapy, the body starts to produce some insulin, which reduces the amount needed from external sources. This decrease can be very welcome, leading to fewer insulin injections and easier blood sugar management. During this phase, individuals often find that their blood sugar levels are more stable, and they experience fewer episodes of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. The reduction in insulin needs can vary widely among individuals, making it crucial to regularly monitor blood sugar and adjust insulin dosages accordingly. It is important to remember that this is a temporary phase, and insulin requirements will likely increase again as the body’s insulin production declines. Managing the honeymoon phase requires a proactive approach to adapt treatment strategies as needed.
Understanding the Reduced Insulin Requirement

Understanding the reduced insulin requirement is crucial to managing the honeymoon phase effectively. It involves realizing that the pancreas still produces some insulin during this phase, supplementing the insulin being administered externally. This residual insulin production helps regulate blood sugar levels, which is why insulin needs are lower. Patients and healthcare providers must be aware of the potential for hypoglycemia, as the body might become more sensitive to insulin. Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential to adjust insulin dosages, as needed. Understanding the reduced insulin requirement also allows patients to experience greater flexibility in their daily routines, dietary choices, and exercise habits. It is important to remember that this phase is temporary and that insulin needs will change over time. Effective management demands a proactive approach to adapt treatment plans and ensure optimal blood sugar control.
Fact 2 Improved Blood Sugar Control
Improved blood sugar control is a hallmark of the honeymoon phase. With reduced insulin needs and some residual insulin production, individuals often experience more stable and predictable blood glucose levels. This can lead to fewer fluctuations, less frequent episodes of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia, and an overall sense of better health. Achieving good blood sugar control during this phase helps prevent the long-term complications associated with diabetes, such as damage to the eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels is essential to maintain this control, and patients should work with their healthcare providers to adjust their insulin doses and lifestyle habits as needed. Maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques further support blood sugar control and overall well-being during the honeymoon phase. Effective management strategies ensure that individuals can enjoy the benefits of this phase while setting a solid foundation for their long-term diabetes care.
Achieving Better Blood Sugar Levels
Achieving better blood sugar levels during the honeymoon phase requires a multi-faceted approach focused on regular monitoring, precise insulin dosing, and a healthy lifestyle. Regular blood glucose checks throughout the day are essential to understand how the body responds to food, exercise, and insulin. Working closely with a healthcare provider to adjust insulin dosages based on blood sugar readings is equally important. Maintaining a balanced diet with controlled carbohydrate intake helps prevent blood sugar spikes, while regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and helps regulate blood glucose levels. It is important to be mindful of the risk of hypoglycemia and be prepared to treat low blood sugar promptly with fast-acting carbohydrates. With diligent monitoring, careful insulin management, and a commitment to a healthy lifestyle, individuals can optimize their blood sugar control, reduce the risk of complications, and enjoy the benefits of the honeymoon phase. It is a proactive effort to build a stable foundation for managing type 1 diabetes long-term.
Fact 3 Pancreas Still Produces Insulin

During the honeymoon phase, the pancreas continues to produce some insulin, which is a key characteristic of this period. This residual insulin production is essential because it reduces the external insulin requirements and makes blood sugar management easier. The amount of insulin produced by the pancreas can vary from person to person. This is why it’s crucial to monitor blood sugar levels and adjust insulin dosages accordingly. The presence of residual insulin provides a degree of protection against extreme fluctuations in blood sugar, which can make it easier for individuals to manage their diabetes. While the pancreas’s insulin production is limited, its contribution significantly affects blood sugar control. Understanding this allows patients to adapt their treatment strategies to best utilize the benefits of the honeymoon phase. This residual function eventually diminishes, so careful management and a proactive approach are essential for ensuring long-term health and diabetes management.
Residual Beta-Cell Function
Residual beta-cell function refers to the remaining insulin-producing capacity of the pancreas during the honeymoon phase. This function varies among individuals, influencing the duration and intensity of the honeymoon phase. Preserving and supporting residual beta-cell function is a key goal in diabetes management. Current research aims to protect beta cells from further destruction. Healthcare providers and patients work together to optimize blood sugar control and reduce the workload on the remaining beta cells. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, can also play a crucial role in supporting beta-cell function. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and adjustments in insulin therapy are essential to manage the benefits of residual beta-cell function, maximizing the duration and positive impacts of the honeymoon phase. Understanding and appreciating residual beta-cell function is critical to creating tailored management plans for each person, promoting better health outcomes and a better quality of life.
Fact 4 Variable Phase Length
The honeymoon phase’s duration varies significantly from person to person, lasting from a few weeks to several months, sometimes even longer. Several factors influence the length of this period, including the individual’s age, the severity of the initial diabetes diagnosis, and the treatment plan. Because the length is unpredictable, healthcare providers and patients must work closely to manage diabetes effectively. It’s important to regularly monitor blood sugar levels and adjust insulin dosages, maintaining optimal control. This variability underscores the need for personalized care. Recognizing that the honeymoon phase will eventually end and proactively planning for the future is crucial. While the exact timing cannot be predicted, understanding the factors that influence this phase allows for more adaptable management strategies. This helps patients manage their diabetes and remain healthy throughout their lives. Adaptability and open communication with the healthcare team are crucial components of effective diabetes management.
Factors Affecting Honeymoon Phase Duration

Several factors influence the duration of the honeymoon phase in type 1 diabetes. The age of the individual at diagnosis can play a role, with some studies suggesting that younger patients may experience a longer honeymoon phase. The initial severity of the diabetes and the degree of beta-cell destruction at the time of diagnosis also contribute to the phase’s length. Early and intensive insulin therapy can help preserve residual beta-cell function and potentially extend the honeymoon phase. The individual’s adherence to a healthy lifestyle, including diet and exercise, also contributes to the maintenance of better blood sugar control. The specific treatment approach, including the type and dosage of insulin, plays a key role. Understanding these influencing factors empowers patients and healthcare providers to develop and maintain a personalized approach to diabetes management. This allows them to adjust the management plan according to the changing needs of the individual and to prepare for the eventual end of the honeymoon phase. The healthcare team must work together to ensure effective diabetes management.
Fact 5 Emotional Impact
The honeymoon phase has a significant emotional impact on individuals diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. The initial diagnosis and the subsequent need for insulin injections can be overwhelming and stressful. The honeymoon phase brings a sense of relief and optimism as insulin needs decrease and blood sugar levels become easier to manage. This can lead to improved mood and a sense of normalcy. This phase can also be challenging as individuals may struggle with feelings of uncertainty, as they know the honeymoon will eventually end. It’s important to address the emotional aspects of diabetes management. Patients should seek support from family, friends, and support groups. Mental health professionals and diabetes educators can provide strategies for coping with the emotional changes. Open communication with the healthcare team allows for discussing any anxieties or concerns. Understanding the emotional toll of the honeymoon phase helps promote overall well-being and enhances the capacity to manage diabetes effectively. This ensures that individuals are well-equipped to navigate the emotional journey associated with the disease.
Managing the Emotional Aspects
Managing the emotional aspects of the honeymoon phase is crucial for overall well-being and effective diabetes management. Recognizing the potential for emotional ups and downs is the first step. Openly communicating with healthcare providers, family, and friends is essential for sharing feelings and concerns. Joining diabetes support groups can provide a sense of community, and people can share experiences. Practicing self-care, including regular exercise, a healthy diet, and adequate sleep, can improve mood and resilience. Seeking professional support from therapists or counselors specialized in diabetes can help develop coping strategies. Practicing mindfulness or relaxation techniques can manage stress and anxiety. Being proactive in managing emotional health allows individuals to navigate the challenges of the honeymoon phase while maintaining a positive outlook. This helps improve the individual’s emotional well-being. Emotional support is as important as physical health in managing type 1 diabetes.
Strategies for Managing the Honeymoon Phase

Effective management strategies are essential for maximizing the benefits and adapting to the changing needs of the honeymoon phase. Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial to track glucose levels. Adjusting insulin dosages under the guidance of a healthcare provider is essential to maintain optimal control. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and stress management also contributes to better management. Open communication with the healthcare team allows for adjustments in treatment plans as needed. Being prepared for the eventual end of the honeymoon phase helps with expectations and future care. Active patient participation in the healthcare team, along with emotional support, helps manage diabetes effectively. A proactive approach and the use of comprehensive strategies ensure that individuals can navigate this phase successfully. This contributes to long-term health and well-being.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring blood sugar levels is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management, especially during the honeymoon phase. Regular monitoring allows individuals to track glucose levels throughout the day. This is essential to see how the body responds to food, exercise, and insulin. This information is crucial for making informed decisions about insulin dosages. Consistent monitoring helps identify patterns and trends in blood sugar levels. People must be mindful of the risk of both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia and be prepared to address both. Using a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) can provide real-time glucose readings, which gives an in-depth understanding of blood sugar fluctuations. Keeping a detailed record of blood sugar readings and discussing them regularly with healthcare providers helps optimize insulin therapy and lifestyle adjustments. Regular monitoring ensures better blood sugar control, reduces the risk of complications, and enhances the overall quality of life for people living with type 1 diabetes. It is a proactive step toward effectively managing and monitoring type 1 diabetes.
Adjusting Insulin Dosage
Adjusting insulin dosage is a key component of managing the honeymoon phase effectively. Insulin needs typically decrease during this phase. Working closely with healthcare providers to determine the right insulin dosage is critical to avoid hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia. Regular blood sugar monitoring provides the data required to determine the correct dosages. Insulin adjustments are based on blood glucose readings, food intake, and physical activity levels. Healthcare providers may recommend adjusting the basal insulin doses or bolus insulin doses. Insulin adjustments must be made gradually to see how the body responds. It’s essential to communicate openly with the healthcare team. They can adjust the dosage, especially as needs change. Adjusting insulin dosages effectively minimizes blood sugar fluctuations, improves blood sugar control, and reduces the risk of both short-term and long-term complications. Insulin management is a core aspect of managing type 1 diabetes during the honeymoon phase.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
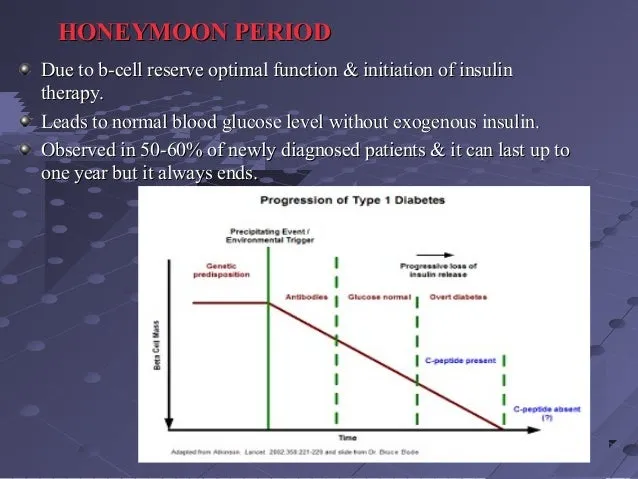
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is an important part of managing diabetes, including the honeymoon phase. A balanced diet focusing on whole foods, lean proteins, and controlled carbohydrate intake helps regulate blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity increases insulin sensitivity and helps the body use glucose more effectively. Exercise can help reduce the amount of insulin needed. Stress management techniques, such as mindfulness and yoga, can help regulate blood sugar levels. Adequate sleep is vital because it influences blood sugar and overall health. Working with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to develop a personalized nutrition plan is a good idea. These lifestyle changes support insulin management and help maximize the benefits of the honeymoon phase. Adopting a healthy lifestyle provides a solid foundation for long-term diabetes management, overall well-being, and enhanced quality of life. Prioritizing these healthy habits is very important.
Conclusion
The honeymoon phase of type 1 diabetes is a unique and often challenging period. It requires a balance of understanding, adaptability, and proactive management. Knowing the characteristics of this phase helps individuals make informed decisions about their health. The reduction in insulin needs, improved blood sugar control, and emotional adjustments are key. Regular blood sugar monitoring, insulin dosage adjustments, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are all essential. The honeymoon phase provides an opportunity to build a strong foundation for long-term diabetes management. By embracing these strategies and working closely with healthcare providers, people living with type 1 diabetes can navigate the honeymoon phase effectively and maintain a positive outlook on their health journey. This approach is important for achieving better outcomes and a higher quality of life.
